Stop guessing what Google wants. After years of building, breaking, and fixing WordPress websites, I’ve learned that the best-ranking sites all follow the same simple SEO principles.
If you’ve ever wondered why your beautifully designed site doesn’t appear on Google — or why random blogs with plain layouts outrank you — this guide is for you.
In this complete WordPress SEO guide, I’ll walk you through everything I do whenever I start a new website — from hosting setup to plugin configuration, keyword research, on-page optimization, and long-term growth.
This isn’t a “quick tips” list. It’s a full-scale roadmap you can actually follow, even if you’re just starting out.
So grab a cup of coffee — we’re about to turn your WordPress site into a Google-friendly, traffic-generating machine.
1. What Exactly Is SEO, and Why It Matters
Let’s start with the basics — because if you understand what SEO really is, you’ll stop wasting time on random hacks.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) means making your website easy for both users and search engines to understand. When Google can clearly figure out what your site is about, it’s more likely to show your content to people searching for it.
SEO is not about tricking algorithms. It’s about making your content so clear, valuable, and technically sound that Google has no reason not to rank you.
Think of it this way:
- You’re building a bridge between your content and people who need it.
- SEO makes that bridge solid, visible, and trustworthy.
Every high-performing website you see online? They’ve all nailed the same fundamentals we’re about to cover.
2. Laying the Foundation: Before You Even Start
Whenever I launch a new project, my first thought isn’t “What should I write?” — it’s “Is my foundation solid?”
Because no amount of keyword research or backlinks can save a website that’s slow, unstable, or poorly structured.
Let’s build that foundation right.
Step 1: Choose Reliable WordPress Hosting
Your hosting is like your site’s engine. If it’s slow, unreliable, or overloaded, it doesn’t matter how good the rest of the car looks — it won’t win any race.
Google uses site speed as a ranking factor, and users are even less patient than Google. Every extra second of loading time increases bounce rate.
When picking hosting, here’s what I always look for:
- SSD storage — forget old HDD servers. SSD is non-negotiable now.
- Server-level caching — your host should offer caching built in.
- Data centers near your target audience — if your readers are in the US, don’t host in Singapore.
- WordPress optimization — managed WordPress hosting usually comes pre-tuned for performance.
Some solid hosts include SiteGround, Hostinger, and Rocket.net.
If you’re still on cheap shared hosting and wondering why your site takes 8 seconds to load — there’s your answer.
Step 2: Pick a Fast, SEO-Friendly WordPress Theme
I’ve made this mistake so many times — falling for a beautiful theme demo that secretly loads 70 scripts in the background.
A theme isn’t just about looks. It’s the backbone of how search engines read your site.
Here’s what to check before you commit:
- Mobile responsiveness: Over 60% of traffic is mobile. If your site doesn’t adapt, Google will penalize it.
- Lightweight code: Skip themes bloated with sliders, animations, or page builders you’ll never use.
- Schema support: Some modern themes include basic structured data (like breadcrumbs) that help SEO.
Good examples? Astra, GeneratePress, Blocksy, and Kadence.
If you’re unsure, install the demo, run it through PageSpeed Insights, and see the score. Anything under 80 on mobile — hard pass.
3. Configuring WordPress for SEO the Right Way
Alright, you’ve got a solid base — now it’s time to configure WordPress itself so Google actually understands what you’re building.
We’ll start with permalinks, then move to plugins and Search Console setup.
Step 1: Set SEO-Friendly URLs (Permalinks)
I still remember when my first blog had URLs like:
https://myblog.com/?p=123Yeah, not great. Neither users nor Google knew what the page was about.
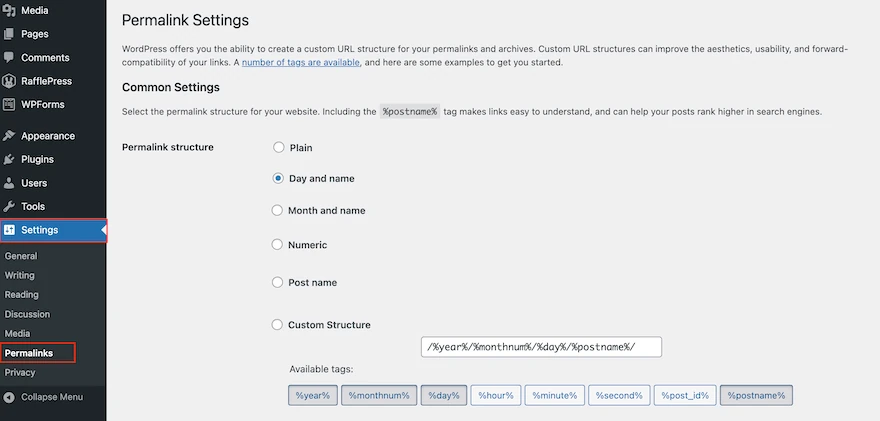
Here’s how to fix it:
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Settings → Permalinks.
- Choose the Post name option ().
/sample-post/ - Save changes.
That’s it — your URLs now describe your content. For example:
https://websitesoez.com/wordpress/configure-nginx-fastcgi-cacheThat’s human-readable, keyword-friendly, and exactly what search engines like.
⚠️ Note: If your site is older than 6 months, changing permalinks may break existing URLs. Use a plugin like “Redirection” to create 301 redirects from old to new URLs.
Step 2: Install a Proper SEO Plugin
Out of the box, WordPress is decent for SEO — but it won’t let you add meta descriptions, control schema, or create XML sitemaps.
That’s where plugins come in.

The two big names are:
- Yoast SEO — the old reliable classic.
- All in One SEO (AIOSEO) — my personal favorite for new sites.
I switched to AIOSEO because it handles structured data better and updates faster.
Once installed, it’ll help you:
- Set custom meta titles and descriptions.
- Generate XML sitemaps.
- Add Open Graph data for social sharing.
- Analyze your content in real time with “TruSEO” suggestions.
It’s like having an SEO coach inside your WordPress editor.
Step 3: Generate and Submit Your XML Sitemap
Your sitemap is like a table of contents for Google. It tells search engines what to index and what to ignore.
AIOSEO automatically creates it at:
https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xmlCopy that URL — we’ll need it for the next step.
Step 4: Connect to Google Search Console
If you’re not using Google Search Console yet, you’re flying blind.
This free tool shows how Google sees your site — what pages are indexed, what keywords you’re ranking for, and any errors or penalties.
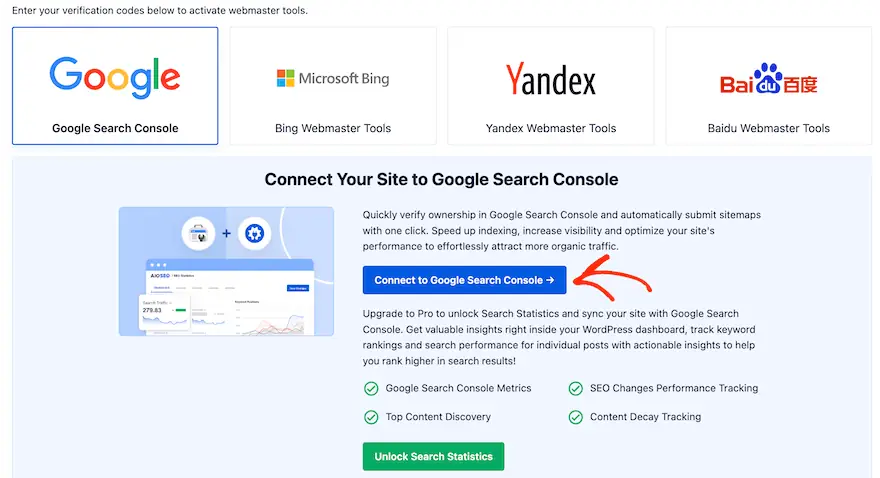
To set it up:
- Go to Google Search Console.
- Add your domain.
- Verify ownership (AIOSEO can insert the code for you).
- Submit your sitemap under Index → Sitemaps.
Within a few days, you’ll start seeing impressions, clicks, and keyword data.
I check my GSC weekly to track progress and fix crawl issues before they hurt my rankings.
4. Keyword Research That Actually Works
Now we get into the part that separates hobby bloggers from sites that rank.
Keyword research isn’t about chasing huge search volumes — it’s about finding realistic opportunities.
When you’re new, targeting “best web hosting” won’t get you anywhere. Competing with giants like WPBeginner or HubSpot is suicide.
Instead, aim for long-tail, low-competition keywords — things like “best WordPress caching plugin for beginners” or “how to fix redirect loop Cloudflare WordPress.”
Tools I use:
- LowFruits.io — shows keywords where weak sites already rank.
- WPBeginner Keyword Generator — free and surprisingly good.
- Google’s autocomplete — still one of the best free tools.
I like to build keyword clusters — 3–4 related posts around one main topic. It helps Google understand you’re an authority in that niche.

Example:
Main topic → WordPress caching
Supporting posts → “Enable NGINX FastCGI cache”, “Best caching plugins”, “How caching improves Core Web Vitals”.
This structure builds topical relevance and helps every article rank better.
5. Writing and Optimizing Posts for SEO
Now that you have keywords, let’s talk about on-page optimization — making each post rankable without killing readability.
When I write, I follow a simple 3-step checklist:
Step 1: Structure Your Content for Readers
Forget about “writing for bots.” Google understands natural language now.
Your job is to make your content enjoyable for humans and easy for algorithms to parse.
Use:
- Clear H2 and H3 headings.
- Short paragraphs (2–3 lines).
- Bullet points or numbered lists.
- Internal links to related posts.
AIOSEO’s “TruSEO” feature helps you ensure the main keyword appears in your title, URL, and intro — without stuffing it awkwardly.
Step 2: Write for Intent, Not Just Keywords
When someone searches “best SEO plugin,” what do they want?
- They’re comparing tools.
- They need pros/cons, maybe screenshots, maybe a recommendation.
Give them that. Satisfy the intent behind the keyword, not just the keyword itself.
This is how you win featured snippets and longer dwell time.
Step 3: Use Schema Markup (Without Coding)
Have you noticed that some search results look completely different? They might display star ratings, small pictures, or boxes containing frequently asked questions.
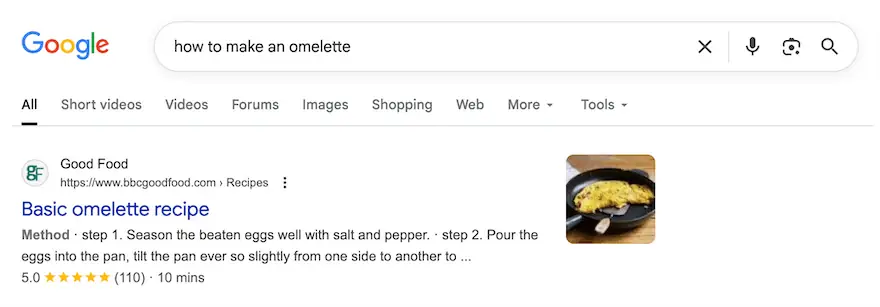
These eye-catching results, known as rich media summaries, are one of the best ways to improve click-through rate (CTR). After all, simply ranking high isn’t enough. You have to win those clicks, and rich snippets can help you stand out.
To increase your chances of getting these rich snippets, you need to use schema tags.
Structured data helps Google show rich results — like FAQs, ratings, or how-to boxes.
AIOSEO lets you add schema directly in the post editor.
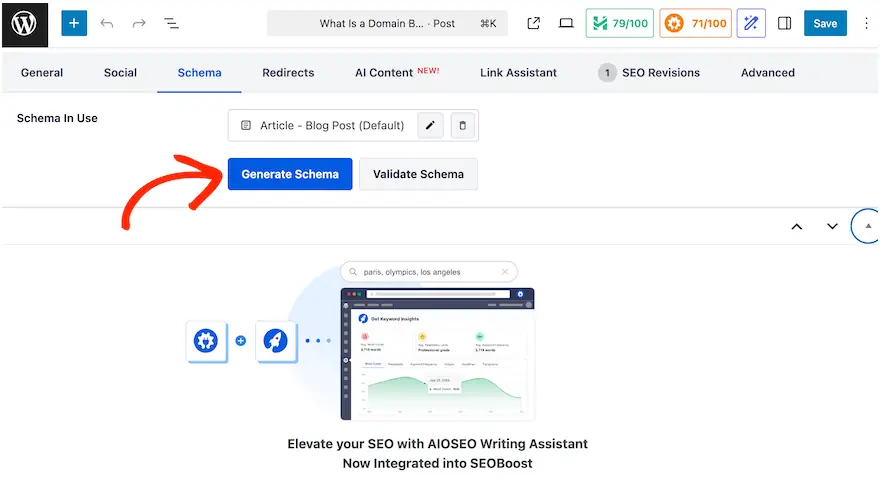
For example, if you’re writing a guide like this one, choose Article schema, or add an FAQ block for extra visibility in search results.
6. Smart Internal Linking
Search engines use “page authority” to measure the importance of each page on your website. While the exact formula used by search engines like Google is unclear, we know that links play a significant role.
A link from one page to another acts like a ticket of trust, transferring authority and relevance to the linking page.
This is why you need a clear plan for linking to your content from other articles. This is called your internal linking strategy.
Here’s a big SEO secret: Your best backlinks are often your own pages.
Internal links pass authority around your site and help Google crawl deeper pages.
I aim for 3–5 internal links per post, ideally from relevant articles.
If you’re using AIOSEO, the “Link Assistant” will automatically suggest posts you can link to — a huge time-saver.
Also, avoid overusing “nofollow” internally. Reserve that for paid or untrusted external links. By selectively using nofollow, you can ensure that your website’s hard-earned SEO value remains focused on your own content.
Linking to relevant, high-quality external websites is a good strategy because it adds direct value to your readers. However, you also need to be strategic. Linking to external websites can decrease your website’s SEO value, even if you are building authority.
This is where the nofollow attribute comes in. When you add the nofollow tag to an external link, you are telling search engines that you do not want to pass your authority to the target site.
7. Performance Optimization: Speed = Rankings
A fast site isn’t just nice to have — it’s a ranking signal.
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure load speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
Install a Caching Plugin
Caching saves pre-built versions of your pages and serves them instantly.
Use WP Rocket, LiteSpeed Cache, or W3 Total Cache — all solid choices.
Optimize Images
Use compression plugins like EWWW Image Optimizer or Optimole.
Stick to WebP format whenever possible.
If your site is image-heavy (like a shop or gallery), consider Envira Gallery — it’s fast and SEO-friendly.
Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network)
A CDN stores your static files on global servers, reducing load time for distant users.
Cloudflare offers a great free plan.
8. Avoid Duplicate Content and Slow Pages
By default, WordPress displays the full text of blog posts in multiple locations on your website. This includes your homepage, category archives, tag archives, and even your author page.
While this seems convenient, it’s actually very bad for your SEO.
When search engines like Google crawl the web, they are looking for unique content. If the exact same article appears in multiple different URLs, the search engine will treat it as duplicate content.
Therefore, Google will choose one version to index and completely ignore the other duplicates. As a result, the page you want to rank for might not be the one indexed and displayed to users.
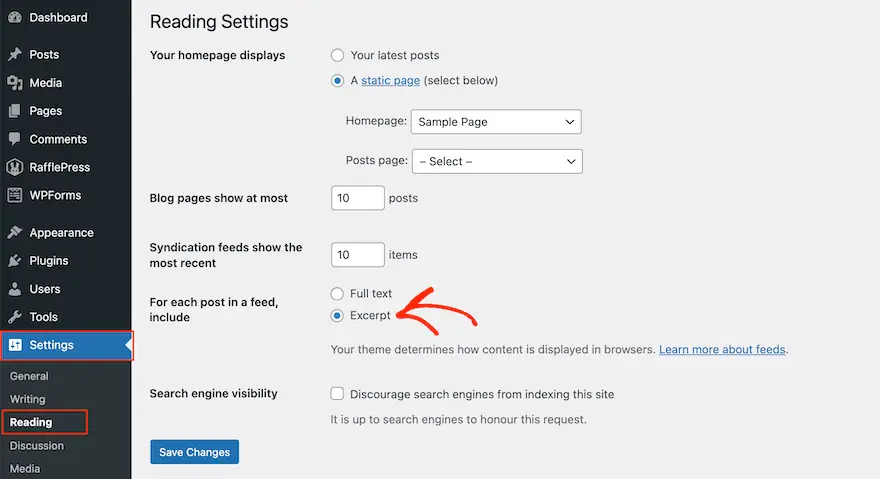
There’s a simple solution: display excerpts instead of the full article.
Excerpts are short summaries of the content, and they immediately solve the problem of duplicate content. They also encourage users to click and view the main article. This is great because it increases your page views and tells Google that people want to read your content.
To display excerpts instead of the full text, go to Settings » Reading in your WordPress dashboard. On this screen, select the radio button next to “Excerpts”.
By using pagination, visitors can read the entire discussion without the server loading hundreds of comments at once. In fact, I tested pagination on a very popular post, and the difference in page load speed was instantaneous and measurable.
To enable pagination, simply go to Settings » Discussions in your WordPress dashboard.
Here, check the box next to “Split comments into pages”. You can now enter the number of comments you want to display on each page.
At this point, you can also use the “First Page/Last Page” dropdown menu to decide whether to display the oldest or newest comments first. When you are happy with your pagination settings, don’t forget to click “Save Changes”.

This simple change ensures that your busy, engaging comment section won’t cripple your search engine optimization.
9. Securing Your SEO Investment
You can spend months building a good ranking, but if your website is hacked, Google may immediately remove you from its search results. If this happens, you will lose all the time and effort you’ve invested in improving your SEO.
Use SSL (HTTPS)
Google treats HTTPS as a ranking factor. Most hosts now include free Let’s Encrypt SSL — activate it.
Strong Passwords + 2FA
Use a password manager like 1Password or Bitwarden, and enable two-factor authentication with WP 2FA.
Keep WordPress Updated
Outdated plugins are hacker magnets. Always update core, themes, and plugins.
Use a Firewall Plugin
Install Wordfence or Sucuri to block malicious bots and brute-force attacks.
Filter Spam Comments
Use Akismet or manual moderation to prevent spam links from diluting your SEO.
10. Long-Term SEO Strategy
SEO is a marathon, not a sprint.
I like to focus on one improvement each week —
optimize images this week, add schema next week, build internal links after that.
Keep publishing consistent, high-quality posts that genuinely help your readers.
When Google sees your site consistently delivers value, your rankings will grow naturally — no hacks required.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve made it this far, you already know more about real WordPress SEO than 90% of beginners out there.
SEO isn’t magic. It’s a system — a combination of technical setup, content strategy, and consistency.
You don’t need to chase algorithms.
Just build a fast, secure, well-structured website that solves problems better than anyone else — and Google will notice.
Now go optimize your WordPress site for Google, step by step.
And when that first organic visitor arrives out of nowhere, you’ll know it was all worth it.
✅ Quick SEO Recap Checklist
- Choose fast hosting (SSD, WordPress-optimized)
- Use a lightweight, mobile-responsive theme
- Set permalinks to “Post name”
- Install AIOSEO and connect to Google Search Console
- Generate XML sitemap and submit it
- Research long-tail, low-competition keywords
- Add schema markup and FAQ blocks
- Build internal links between posts
- Cache your site and optimize images
- Secure with SSL, 2FA, and regular updates
Do these consistently, and your WordPress SEO will snowball — trust me, I’ve done it dozens of times.