If you’ve ever launched a new website and watched Google Search Console day after day, you’re probably familiar with this frustration:
Your SEO plugin is configured correctly.
Your sitemap is submitted.
Google Search Console shows your pages…
But your website is not indexing.
For many site owners, this turns into endless tweaking—changing Yoast or RankMath settings, rewriting pages, resubmitting sitemaps—without real progress.
Here’s the reality most tutorials don’t explain clearly:
Most “website not indexing” problems are not caused by SEO plugins. They are caused by conflicting index signals or weak quality signals that Google doesn’t trust yet.
SEO plugins don’t force Google to index pages. They only help you communicate indexing signals. Whether Google accepts those signals depends on consistency, crawlability, and content value.
This guide walks through how to fix website indexing issues step by step, using the same troubleshooting order I use on real sites—especially new domains.
Step 1: Start With Google Search Console Troubleshooting (Before Changing Anything)
When people see “Google not indexing pages,” they usually start changing settings immediately. That’s backwards.
Your first step should always be Google Search Console troubleshooting, specifically the URL Inspection tool.
This is Google’s own explanation of why a page is excluded. It’s more reliable than assumptions or plugin advice.
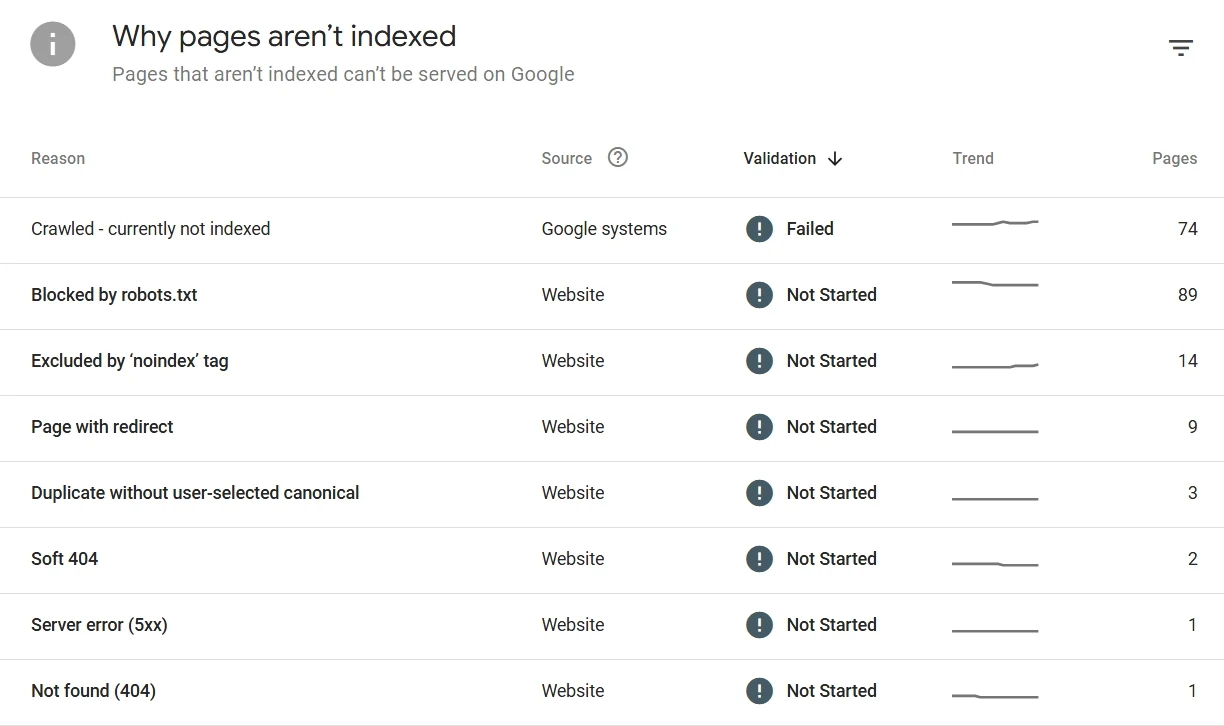
Common Indexing Statuses and What They Actually Mean
Understanding these messages is critical to fixing website indexing issues correctly:
- Discovered – currently not indexed
Google knows the page exists but hasn’t decided to index it yet. This usually means low priority, low trust, or unstable signals. - Crawled – currently not indexed
Google has already read the page but decided it doesn’t add enough value or the signals are inconsistent. - Blocked by robots.txt
Google is not allowed to crawl the page. - Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
You explicitly told Google not to index the page. - Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical
Google considers the page a duplicate and indexed another version instead.
Important:
Each status requires a different solution. Treating them the same is why many “fix website indexing” attempts fail.
Step 2: The Three Indexing Kill Switches That Break New Websites
In most cases, the reason a website is not indexing has nothing to do with content quality yet. It’s usually caused by one of these switches.
2.1 WordPress Global Indexing Setting (The Most Common Mistake)
Path:
WordPress → Settings → Reading → “Discourage search engines from indexing this site”
If this box is checked, WordPress outputs a site-wide noindex signal.
Even if RankMath, Yoast, or SEOPress says “index enabled,” Google will still see noindex.
If you’re trying to fix website indexing problems, always check this first.
2.2 SEO Plugin Global noindex Misconfiguration
Even experienced users accidentally disable indexing at the content-type level.
RankMath / Yoast / SEOPress – What to Check
Focus on:
- Posts
- Pages
- Products (if WooCommerce is installed)
A single global noindex setting here can prevent every page of that type from being indexed.
This is one of the most common reasons Google Search Console shows:
- Pages discovered but not indexed
- Google not indexing pages despite sitemap submission
2.3 Individual Pages Set to noindex
Even if global settings are correct, individual pages may still be blocked.
How to check:
- Open the page editor → SEO settings panel
- Or view source code and search for:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
One hidden noindex tag is enough to stop indexing completely.
Step 3: Canonical Errors That Quietly Prevent Indexing
If noindex is a hard stop, canonical errors are a silent redirect.
A canonical tag tells Google which version of a page should be indexed. When misused, Google simply ignores the page—even though it’s crawlable.
Common Canonical Mistakes
- Multilingual pages canonicalized to the main language
- Filtered or parameter URLs canonicalized to the homepage
- Pagination pages canonicalized incorrectly
In Google Search Console, this often appears as:
“Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical.”
Canonical Rule for Fixing Website Indexing
If you want a page indexed, its canonical URL must point to itself.
Anything else tells Google, “This page is not the main version.”
Step 4: How to Fix Google Crawl Errors Hidden Outside the Page
If indexing still fails, you need to look deeper—beyond page-level SEO.
4.1 robots.txt Blocking Google Crawl
Check:yourdomain.com/robots.txt
Common mistakes include:
- Blocking
/wp-content/ - Blocking
/blog/or/product/
If Google can’t crawl a page, it can’t index it. This is one of the most overlooked Google crawl errors.
4.2 X-Robots-Tag in HTTP Headers (Advanced but Dangerous)
Some cache plugins, security plugins, or CDNs add this header:
X-Robots-Tag: noindex
This overrides:
- Meta robots tags
- SEO plugin settings
- robots.txt allowances
If you’re trying to fix website indexing issues and nothing makes sense, always check response headers.
Step 5: Why Submitting a Sitemap Doesn’t Fix Indexing
A sitemap only tells Google which URLs exist.
It does not guarantee indexing.
Google still ignores pages that:
- Are duplicated
- Have no internal links
- Are orphan pages
- Lack topical relevance
This is why many people see:
“Sitemap submitted successfully”
but their website is not indexing.
Step 6: SEO Plugins Don’t Cause Indexing Problems—Misuse Does
RankMath, Yoast, and SEOPress all handle indexing signals correctly.
Problems arise when:
- Global noindex settings are enabled unintentionally
- Canonicals are misunderstood
- Users expect plugins to “force” indexing
Plugins control signals. Google makes the final decision.
Step 7: When Everything Is Technically Correct but Pages Still Aren’t Indexed
If:
- No noindex tags exist
- Google can crawl the page
- Canonicals are correct
- No crawl errors appear in Google Search Console
Then the issue is no longer technical.
At this point, Google is evaluating value and trust.
The Three Real Reasons Google Won’t Index Yet
- No unique value
Your content doesn’t add anything new to the index. - Weak internal linking
Google doesn’t see the page as important. - Low domain trust (new site delay)
New sites often go through an observation phase.
No plugin setting can fix this.
Final Thoughts: Fix Website Indexing by Fixing Signals, Not Chasing Settings
If your website is not indexing, the solution is rarely “install another SEO plugin.”
Indexing happens when:
- Signals are consistent
- Crawl paths are open
- Canonicals make sense
- Content deserves a place in the index
Once you stop fighting Google and start aligning signals, indexing stops feeling random—and becomes predictable.
Most indexing issues aren’t mysterious.
They’re just misdiagnosed.
Follow a structured Google Search Console troubleshooting process, fix real crawl errors, and focus on value.
That’s how you actually fix website indexing problems—long term.
Further Reading: Supercharge Your Site with CMS Structure – No Fancy Plugins Needed!


