Whether you are building a large enterprise website, launching a global e-commerce platform, or running a content-driven media site, as of 2025, Magento, WordPress, and Drupal remain among the top ten most widely adopted CMS platforms globally.
This article aims to introduce the fundamentals of Magento, WordPress, and Drupal and compare them across functional architecture, e-commerce capabilities, SEO advantages, security, scalability, and cost, helping businesses select the CMS that best suits their specific needs.

1. Market Overview of the Three CMS Platforms
1.1 Market Positioning
WordPress: The world’s leading multi-purpose CMS
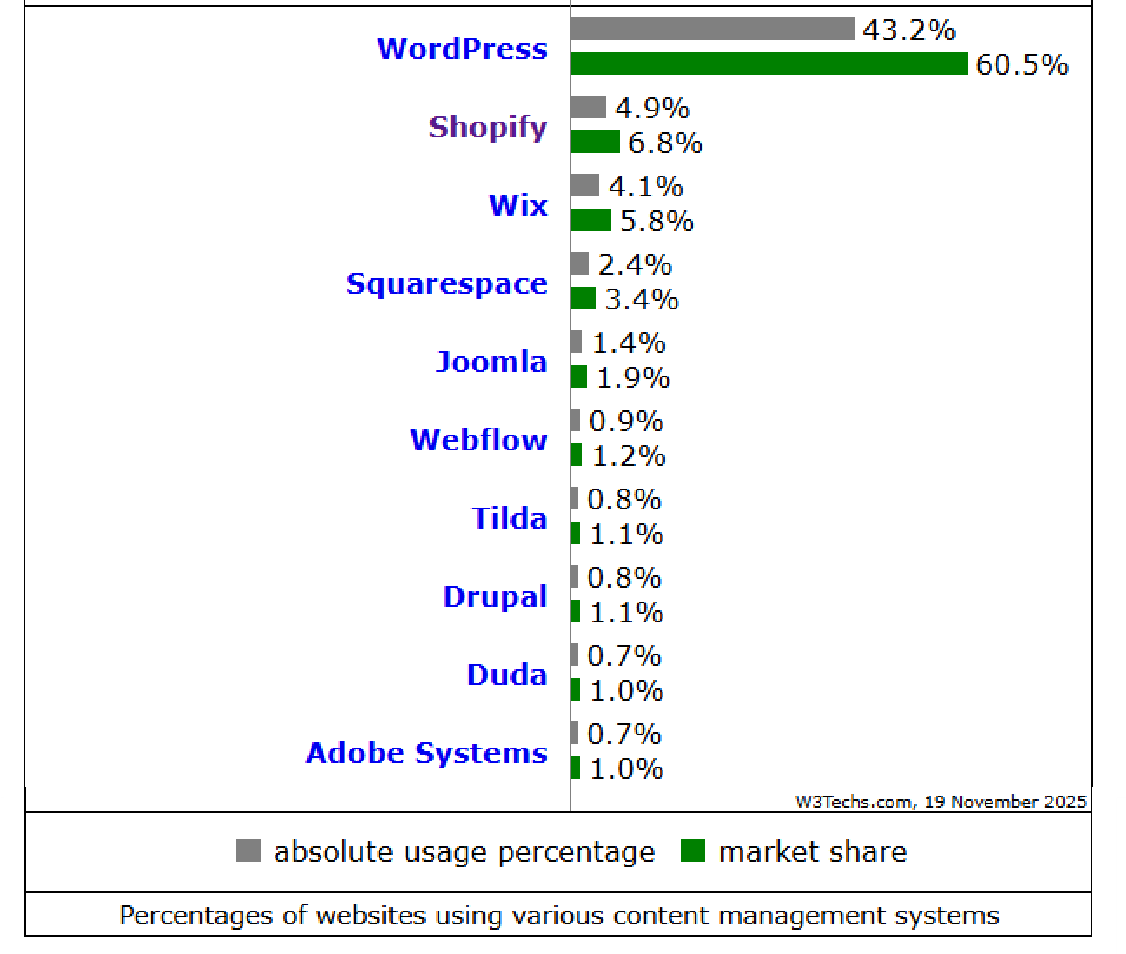
WordPress powers over 43% of all websites worldwide. It is highly flexible, boasts the largest plugin ecosystem, and is extremely beginner-friendly. It is suitable for blogs, corporate websites, portals, membership sites, and e-commerce stores—essentially any type of web project.
Magento: Professional E-Commerce CMS
Magento (Adobe Commerce) is primarily used for medium to large e-commerce sites. It features highly scalable e-commerce capabilities, multi-warehouse support, complex promotion rules, multi-currency, and multilingual support. Backed by the Adobe ecosystem, Magento is a leading enterprise-level e-commerce CMS.
Drupal: Enterprise Content Management Specialist
Drupal is a CMS known for its security and flexibility, suitable for government websites, publicly traded companies, universities, and other large institutions. It excels in complex permission management, structured content, and multi-language sites.
1.2 Market Share in 2025
As of 2025, WordPress remains the market leader, accounting for 60.5% of CMS usage.
| No. | Platform | Market Share | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WordPress | ~60.5% | W3Techs, October 2025, Usage statistics and market shares of content management systems |
| 2 | Drupal | ~1.5% | Global Media Insight, Drupal Statistics 2025 |
| 3 | Magento | ~0.8% | 2024–2025 E-commerce CMS market data |
2. Functional Architecture Comparison: Stability vs Flexibility
WordPress: Strongest Plugin Ecosystem
- Over 60,000 plugins for unlimited functionality expansion
- Intuitive visual editors (Elementor, Gutenberg)
- Rich theme system with high design freedom
- Most user-friendly for non-technical users
- Ideal for content-heavy websites that need to launch quickly
Magento: Highly Customizable E-Commerce Architecture
- Native support for multiple stores, currencies, and languages
- Powerful promotion rules engine
- Complete order and inventory management
- Built-in e-commerce features surpass most CMS, supporting high concurrency and large transaction volumes
Drupal: Modular and Highly Extensible
- Detailed content type definitions
- Flexible permission management system
- Strong API integration capabilities
- Best suited for websites with complex structures, multiple content models, and strict permission systems
3. E-Commerce Capabilities: Magento Takes the Lead
Magento: Most Feature-Rich for E-Commerce
- Native support for complex product types
- Built-in B2B features
- High-performance order processing
- SEO-friendly URLs and structure
Magento is ideal for international e-commerce and B2B platforms.
WordPress + WooCommerce: Flexible and Lightweight
- Easy installation and fast to learn
- Extensive plugin ecosystem and controllable costs
- Suitable for small to medium e-commerce businesses
- WooCommerce allows easy feature expansion but is less suitable for high concurrency, complex SKUs, and international deployments compared to Magento
Drupal Commerce: Stable but Smaller Ecosystem
- Deep integration of content and commerce
- Highly customizable shopping experience
- Suitable for complex business logic scenarios
- Ideal for content + e-commerce hybrid websites, though the plugin ecosystem is smaller than WooCommerce or Magento
4. SEO Performance: WordPress and Drupal Excel

WordPress: Mature Plugins, Beginner-Friendly SEO
- Yoast SEO and Rank Math make SEO adjustments simple and effective
- Comprehensive metadata management
- Perfect for content marketing-focused websites
Drupal: Structured Content, Technical SEO Powerhouse
- Excellent URL structure, taxonomy, and multilingual SEO
- Well-suited for large enterprises
Magento: SEO Depends on Extensions
- Product structure is SEO-friendly
- Requires professional extensions for full functionality
- Content management for SEO is weaker than WordPress
5. Security Comparison: Drupal Leads

Drupal: Government-Level Security
- Used by many government institutions, universities, and financial organizations
- Strong security and strict permission systems
Magento: Enterprise-Level Security
- Suitable for large-scale transactions
- Maintenance costs are high
WordPress: Risk Increases with Plugins
- Core is secure, but outdated plugins/themes can be vulnerabilities
- Requires regular updates and firewall protection
| No. | Platform | Security Features | Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WordPress | Core security is good; plugins need careful management; regular updates are crucial | Low cost; abundant resources | Outdated plugins/themes are vulnerable; community patches needed |
| 2 | Drupal | Government-level security; strict code review; enterprise permission management | Highly structured; very secure | High development cost; steep learning curve |
| 3 | Magento | Native payment security; regular patch updates; requires professional team | Strong e-commerce features; highly extensible | Vulnerable if patches delayed; high maintenance cost |
6. Scalability Comparison: Magento and Drupal for Large Projects
- WordPress: Strong for content + light e-commerce, but not ideal for ultra-large-scale e-commerce
- Magento: Designed for large e-commerce projects; handles high concurrency, massive SKUs, and complex product logic; widely used by world-class brands
- Drupal: Best for complex portals and multi-user websites; excels in multi-language support, large information repositories, and complex content models
7. Cost Comparison: WordPress Cheapest, Magento Most Expensive
- WordPress: Lowest cost; suitable for businesses with limited budget and flexible operations
- Magento: Highest cost; best for medium/large companies or high-growth e-commerce ventures
- Drupal: Moderate cost; suitable for organizations with high security and structured content requirements
| No. | Cost Aspect | WordPress | Magento | Drupal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Setup | Lowest | Highest | Higher than WordPress |
| 2 | Maintenance | Relatively low | Expensive | Requires professional support |
| 3 | Technical Team | Themes/plugins cost-controllable | Requires professional team | Professional support needed |
| 4 | ROI | Best cost-performance | Heavy investment | Stable long-term ROI |
Conclusion: Which CMS Is Right for You?
In 2025, the best strategy is not to blindly choose a CMS. Selection should be based on your business goals, project size, budget, and future scalability.
Magento, WordPress, and Drupal are all powerful, each with its ideal use case:
| No. | Category | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Launch Speed | Very fast; rich plugins; easy | Moderate; needs structured planning | Slowest; most complex setup |
| 2 | Cost | Lowest (hosting + plugins) | Medium-High (requires team) | Highest (development + operations + hosting) |
| 3 | Scalability | Medium (plugin ecosystem strong, but not ultra-large) | High (structured content + permissions) | Extremely high (best for e-commerce) |
| 4 | Security | Depends on plugins/updates | Very high (government standard) | High (but vulnerabilities impactful) |
| 5 | SEO Capability | Strongest (Yoast, Rank Math, speed optimization plugins) | Strong (structured content-friendly) | Medium (needs 3rd-party SEO plugins) |
| 6 | E-Commerce | WooCommerce for small/medium | Drupal Commerce for content + commerce hybrid | Leading enterprise-level e-commerce |
| 7 | Best Use Case | Blogs, media, e-commerce, SMBs, mid-sized content sites | Government, large enterprise portals, educational institutions | B2B/B2C, large international e-commerce |
